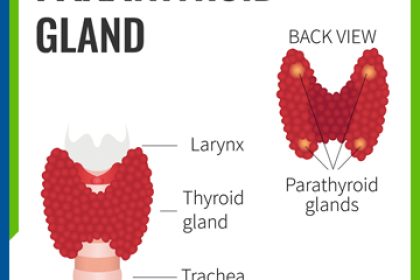
Parathyroid glands are 2-3 mm in size, located behind thyroid glands, and there are normally 4 glands locating 2 on the left and 2 on the right. Parathyroid hormone is briefly defined as parathormone (PTH). There may be some problems (such as hypoparathyroidism, hyperparathyroidism) associated with parathyroid glands which play important role in our general health status.
-
Parathyroid Adenoma
Parathyroid adenoma is defined as a benign tumor which causes excessive parathormone secretion, leading to high levels of calcium in blood. Parathyroid adenoma is treated surgically. This treatment procedure is based on the principle of removing problematic parathyroid gland, and returning blood calcium levels back to normal. Excessive parathormone secretion due to parathyroid adenoma may expose the body to high calcium levels, affecting all systems and leading to serious problems.
Parathyroid adenoma can be seen in all age groups of men and women however, it is most frequently found in elder women in post-menopausal period. The exact cause is unknown. Parathyroid gland locations should be identified and the disease must be clearly diagnosed for the patients who will undergo surgical treatment due to symptoms and discomfort caused by parathyroid adenoma. Ultrasound scan and MIBI scintigraphy are often preferred methods to localize the adenoma. Surgical treatment becomes easier if adenoma can be clearly localized. Exact location of parathyroid adenoma cannot be identified in rare cases. This may delay the treatment process.
Parathyroid Adenoma Treatment
Parathyroid adenoma, increases parathormone secretion. Thus, blood calcium levels increase (hypercalcemia). Hypercalcemia causes problems such as osteolysis and fractures in later stages, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, kidney stone formation, stomach problems, fatigue, constipation, vision problems, weakness and high blood pressure.
Parathyroid adenoma can be sometimes confused with other diseases in diagnosis. For instance, as it causes bone and muscle pain, it can be confused with rheumatism or psychological problems due to calcium imbalance. Radiological scan may help diagnosis.
Surgical Treatment in Parathyroid Adenoma
Surgical procedure for parathyroid adenoma should be performed by experienced specialized surgeons. Definitive diagnosis must be carried before the surgery. Once the parathyroid adenoma is located through radiological scans (ultrasound, scintigraphy, computerized tomography, magnetic resonance), its pathology will be identified.
Minimal invasive procedure is primarily preferred if the parathyroid adenoma can be localized before the surgery. Often, adenoma is removed from a 3 centimeters incision, using radionuclide mapping. This procedure enables short operative times and rapid post-operative recovery.
Minimal invasive parathyroidectomy (MIP) can provide up to 95% success rate if performed by experienced professionals and if the patient is properly selected. After carrying diagnosis through biochemical tests, if presence of adenoma of single parathyroid gland can be identified using ultrasound and/or scintigraphy, a small incision on that identified parathyroid gland is made and the gland is surgically removed. Success of MIP procedure depends on pre-operative localization of parathyroid adenoma. Advantages of this procedure are minimal post-operative pain, better cosmetic results, short hospitalization, rapid recovery and possibility of local anesthesia if requested.
An alternative method that enhances MIP success is the use of ROLL (radio-guided occult lesion localization) in the course of surgical procedure. In the morning of surgery, a radionuclide material is injected in the parathyroid adenoma under ultrasound scan. During surgery, the injected substance is traced using a handheld device called gamma probe to enable direct identification of the lesion. This method shortens surgery time and increases success.
If the diagnosis of parathyroid adenoma is delayed, other three parathyroid glands are suppressed because of high parathormone levels, and problems due to extended suppression may arise even after a successful surgery. Calcium and Vitamin D supplements can be prescribed temporarily after the surgery. Post-operative monitoring of calcium levels is crucial.
Calcium deficiency that may occur after the surgery may cause tingling sensation around lips, numbness on fingertips and sometimes contractions, and bone pain. Calcium and Vitamin D supplements administered to those experiencing temporary calcium deficiency usually do not require hospitalization, and can be taken at home.
Surgical procedure success is high in parathyroid adenoma treatment. Most patients are discharged from hospital on the day of procedure or the following day.
An experienced surgeon plays vital role for best planning as well as successful results in parathyroid adenoma treatment.
-
Parathyroid Cancer
Parathyroid cancer is a rare malignant tumor in parathyroid gland, corresponding to only 1-3% of all primary hyperparathyroidism cases. Serious clinical issues such as bone disease, kidney disease and hypercalcemia crisis can be observed during diagnosis, while some patients do not demonstrate any symptoms.
It is often difficult to carry diagnosis before or during operation, it can be confused with parathyroid adenoma, and can be fatal due to relapses after insufficient surgical procedure, local invasions, organ (liver, lung) metastases and hypercaelcemic crisis. The treatment must be carried out by experiencd surgeons and oncologists.
Although radiation exposure in the neck area, certain sporadic and genetic tumors are blamed for ethiology, the exact cause of parathyroid carcinomas is yet unknown.