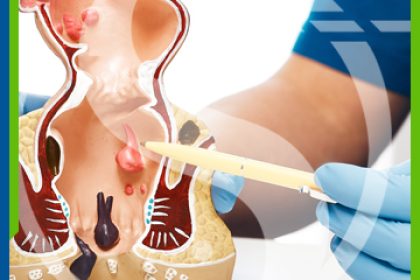
Hemorrhoid tissue is the painful condition which may involve bleeding, and occurs due to swelling of vascular structures located at the bottom end of rectum inside the duct, supported by connective tissue pads, resulting from various reasons. Internal hemorrhoids are vascular complexes on the dentate line, a mucosal borderline located at 2,5-4 cm distance from anus entrance, while external hemorrhoids occur under anal duct anoderm.
Physiopathology of symptomatic hemorrhoids is associated with filling and clogging of the veins in hemorrhoidal network that subsequently stretches and enlarges.
Vascular structures are filled with blood upon exertion of pressure on pelvic base by straining during bowel movement, lifting heavy loads or standing. It mostly occurs during bowel movement due to local traumas in the area. Constipation, extended straining, increase in internal abdominal pressure and weakening of support on the pelvic base together contribute to development of abnormal hemorrhoidal tissues.
Internal Hemorrhoids
 Internal hemorrhoids are covered under mucosa, they typically bleed, protrude but they are not painful. Patients complain about sense of stuffiness in rectal area, presence of mucus in feces, drops of blood in toilet or on toilet paper.
Internal hemorrhoids are covered under mucosa, they typically bleed, protrude but they are not painful. Patients complain about sense of stuffiness in rectal area, presence of mucus in feces, drops of blood in toilet or on toilet paper.
Internal hemorrhoids may swell and tighten in the exterior circle of anal duct, resulting in thrombosis or necrosis.
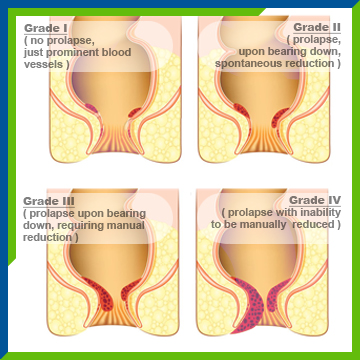
Internal hemorrhoids can be classified as follows: stage one hemorrhoids bleed; stage two hemorrhoids bleed and protrude but spontaneously reduce; stage three hemorrhoids bleed, protrude but can be pushed back in manually; stage four hemorrhoids bleed, tighten outside the anus, and cannot be pushed back manually.
External Hemorrhoids
External hemorrhoids may swell under anal skin in time due to dilatation or repeated thrombosis. Outer skin strains, resulting in protruding skin (skin tag).
Sometimes a clot within external hemorrhoid may cause severe pain, and bleeding may occur if the skin is worn out.
Internal hemorrhoid rarely causes pain unless it causes straining or thrombosis occurs. On the other hand, external hemorrhoids cause pain even after a minor thrombosis because they are located under skin with sensitive nerve ends.
Hemorrhoid symptoms are limited. It is important that a wrong diagnosis is not carried due to misevaluation of other anorectal issues as hemorrhoid.
Treatment
Medical Treatment
Bleeding in stage one and two hemorrhoids can be controlled by including high fiber foods in your diet, use of laxatives, ointments and suppositories or by avoiding standing for extended time or straining during bowel movement. It is important to drink sufficient amount of water together with high fiber food.
In case the medical treatment fails, mechanical treatments such as elastic ligation, classical surgery, laser, transhemorrhoidal dearterialization (THD) is administered for hemorrhoids in stage two and higher.
Elastic Ligation (Rubber Band)
Elastic ligation is a very effective procedure that controls bleeding and prolapsus (sagging) in stages two and three internal hemorrhoids.
The tissue becomes necrotic, withers and falls out, leaving a scar tissue in banding area. This scar tissue prevents subsequent hemorrhoid development, prolapsus and bleeding. Extraordinary pain, fever, difficulty in urinating may occur in the first 12 hours.
Excisional Hemorrhoidectomy
Classic surgery should be restricted to large hemorrhoids, stages three and four hemorrhoids.
Excision procedure should be used for mixed hemorrhoids with external anoderm component which do not permit outpatient treatment or ligation as well as acute thrombosis hemorrhoids and painful, incarcerated hemorrhoids bearing the risk of gangrene. Procedure is performed under general anesthesia. Surgery procedure is not employed for stage one hemorrhoids.
Excision of External Hemorrhoid with Thrombosis
Patients who report to emergency service with an acute hemorrhoid with thrombosis are treated by excision of thrombosis tissue. It is performed under local or general anesthesia.
Longo Hemorrhoidopexy
It is a very effective procedure involving use of stapler, invented and employed by Dr. Longo. It is very effective in advanced stages of hemorrhoid that involve anal mucosa prolapsus.
Laser assisted Hemorrhoidopexy
The procedure which has become popular in recent years is often administered to stage 2 or 3 hemorrhoids, and preferred for less bleeding and pain compared to open surgeries. Results of the procedure start developing in the 3rd week after the procedure. It is performed under general anesthesia.
Transanal Hemorrhoidal Dearterialization (THD)
It is a very effective procedure used for internal hemorrhoids as well as uncomfortable anal mucosa prolapsus. During the procedure, Doppler Ultrasound method is used to find the artery that supplies the hemorrhoid, and the artery is banded by suitable means to prevent blood circulation to hemorrhoid, and the mucosa at the same location is hung on anal duct wall for immediate treatment of anal prolapsus. It is performed under general anesthesia.
Prevention
Most hemorrhoids are the result of poor bowel habits. Plenty of water should be consumed along with high fiber food, and hemorrhoids may relapse due to straining or extended time in toilet.